Effective Summer Cooling
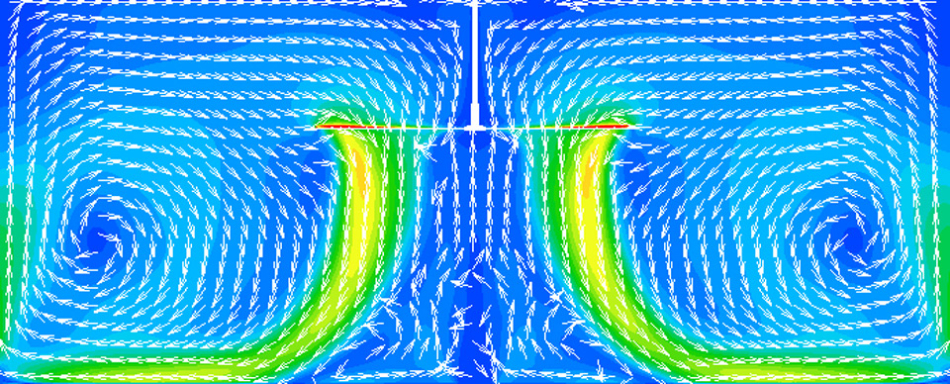
Computational Fluid Dynamics (CFD) analysis shows how cooling is provided in warm buildings when the fan runs in the forward direction. Note the air column produced as well as the air velocities in the enclosed room. As air hits the floor, a wall of air moves away from the center of the fan, cooling the surrounding area.
Winter Heating (Reverse Mode)
Computational Fluid Dynamics (CFD) analysis shows how heating is efficiently provided when the fan runs in the reverse direction. The fan destratifies the space in an enclosed room by mixing air temperatures throughout different air levels. As the fan runs, air is moved toward the walls, forcing warmer air down to ground level. When combined with heated makeup air, or space heating, the space is heated comfortably and efficiently.
Winter Heating Slow Forward Mode
Computational Fluid Dynamics (CFD) analysis shows how heat is dispersed throughout the enclosed space when the fan runs slowly in forward mode. Warm air trapped in the ceiling is mixed with cooler air below to efficiently heat the space.